Ensuring secure and reliable links for their branches
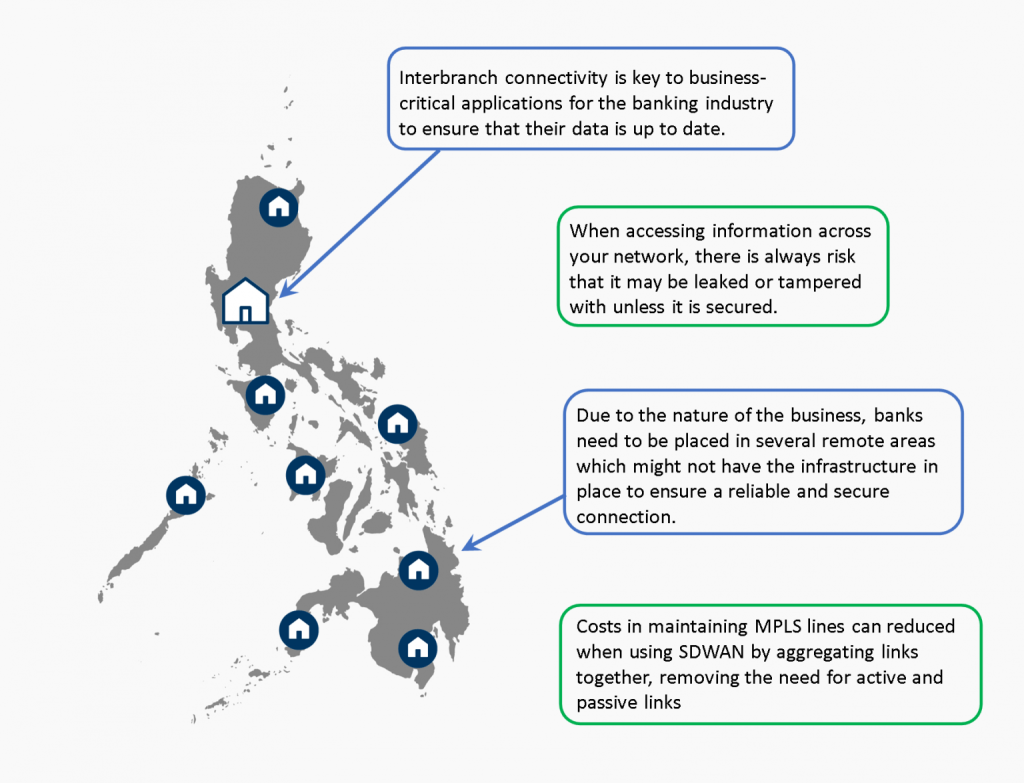
As the demand for banking services increases, banks are rapidly expanding, and their branches are now located in remote areas. While this is a great way to serve more people, it comes with its own set of challenges. One of the most significant challenges is connectivity issues due to the lack of infrastructure for faster links. This can result in slow application performance and delayed information, which can ultimately hinder business operations and cause client dissatisfaction.
Fortunately, there is a solution that can help banks overcome these challenges: SD-WAN. SD-WAN stands for Software-Defined Wide Area Networking, and it is a new way of building and managing networks. SD-WAN technology allows banks to optimize their WAN (Wide Area Network) through link aggregation, WAN optimization, and application prioritization. By using SD-WAN, banks can increase the speed and reliability of their network connections, even in remote areas.
One of the key benefits of SD-WAN is its ability to optimize network performance. With traditional WAN connections, network performance can be impacted by distance, latency, and bandwidth limitations. SD-WAN addresses these issues by providing a more intelligent and dynamic approach to network management. With SD-WAN, banks can prioritize business-critical applications and route traffic based on the most efficient path, optimizing network performance and ensuring fast, reliable access to applications and data.
Another benefit of SD-WAN is its ability to provide multiple link aggregation. With multiple links, banks can improve their network’s availability by providing redundancy and failover capabilities. This means that if one link fails, traffic will automatically be routed to another link, ensuring uninterrupted network access.
Finally, SD-WAN can also help banks reduce their costs by consolidating their infrastructure and providing centralized management. With SD-WAN, banks can use commodity internet links instead of more expensive dedicated circuits, reducing costs while still maintaining high network performance.
To learn more about improving your business, contact us at 8893-9515 or fill out the form below!
By clicking “Submit,” you agree to our Privacy Policy and consent to the collection and use of your personal information as described therein.
